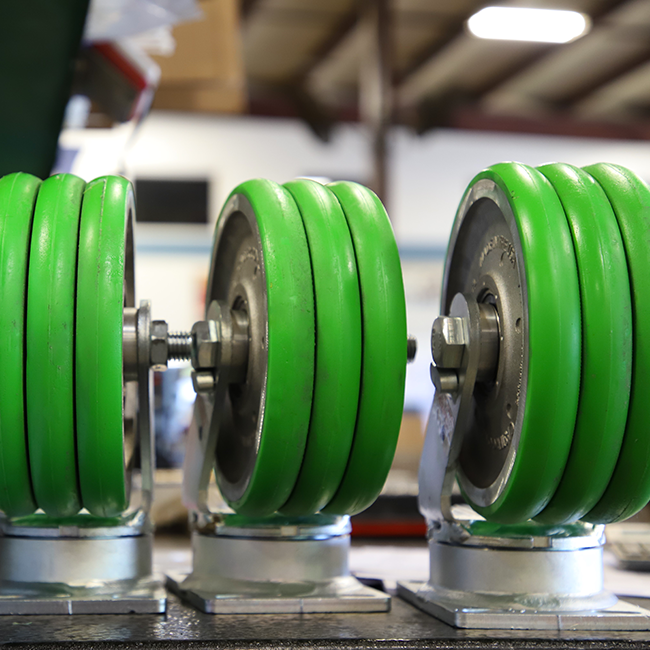


Polyurethane’s debut half a century ago wasn’t just a subtle ripple in the industry pond—it was a monumental splash! The new invention affected plenty of industries, but no other creation had more impact than polyurethane wheels and heavy-duty industrial casters. If you were to take a deep dive into the number, you’d see that a whopping 80% of heavy-duty tasks call for a polyurethane tire paired with a wheel core. It’s the impeccable quality of material and craftsmanship that gives these wheels their long stride.
Allow me to illuminate five pivotal insights about polyurethane wheels. Keep these in mind, and your industrial endeavors are bound to roll smoothly!
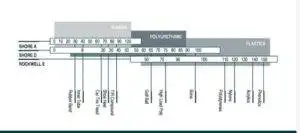
Industrial polyurethane isn’t your garden-variety kind. It’s the heavyweight champ, surpassing its non-dynamic counterparts. Polyurethanes come in different levels of hardness, which is measured in durometers. The higher the number on the durometer scale, the greater the wheel’s resistance to indentation. Standard durometers range from 70 shore A, which is slightly harder than typical rubber materials, to 70 shore D, which is as hard as a bowling ball and designed to maximize weight capacity.
![]() What should be on your checklist?
What should be on your checklist?
With polyurethane wheels, you have to mind the heat. Throw your polyurethane wheels in high heat or environments, and you’ve got its kryptonite. Your typical urethane can only tolerate ambient heat of about 230°F for an hour or so. The higher the heat, the quicker your tires risk melting like ice cream.
Hot casting is the gold standard when producing industrial wheels. When urethane is cast hot (picture a toasty 140-170°F pour, followed by a 190-240°F cure), you’ve got a wheel ready to face the industrial gauntlet. Room temperature processing can save manufacturers money in production but will cost them dearly in caster performance. Caster-Concepts-Hardness-Comparison-Chart

Poly bond failure
One of the most difficult things about polyurethane caster wheels is that their defects come from the inside – at the junction where urethane and core (be it steel or cast iron) meet. A compromised bond is often the weak link. You can’t just see this kind of defect, but your performance will feel it. So, how do you avoid defects? Opt for a manufacturer like Caster Concepts who has a proven ISO 9001-2015 certification and follows established procedures combined with a quality management system.
Polyurethane is a mixture composed of isocyanates and curing agents. You can’t just mix them willy-nilly; it’s about achieving a sweet spot in the ratio of the two. Stoichiometry is the measurement of the ratio of the two components, and a bad ratio will produce a wheel that looks the part but falls flat in function. Many of today’s modern machines include high-tech metering systems and mixers that make the manufacture of a standard stoichiometry mixture a consistent outcome.
Now that you have a better understanding of polyurethane wheels, do they sound like a solution for your mobility needs? Speak with one of our team members about your application, and we can help guide you into a caster that meets your needs and budget. Let’s figure it out together!